How Long Does It Take to Read 1000 Words? — The Complete Reading Time Guide
Learn exactly how long it takes to read 1000 words based on your reading speed (WPM). Explore real examples, categories, and charts showing reading time by purpose and audience.
If you’ve ever asked yourself, “How long does it take to read 1000 words?” — you’re not alone.
Knowing your reading time is essential whether you’re writing a blog post, preparing an audiobook, creating e-learning content, or practicing public speaking.
At WordToTime.org, we built a system that helps you convert word count into reading or speaking time with scientific precision — based on your unique WPM (Words Per Minute).
Let’s break down exactly how long it takes to read 1000 words, what factors change that time, and how to measure your own reading speed.
1. The Short Answer
| Reader Type | Average Speed (WPM) | Time to Read 1000 Words |
|---|---|---|
| Slow reader | 100 WPM | 10 minutes |
| Average reader | 200 WPM | 5 minutes |
| Fast reader | 300 WPM | 3.3 minutes |
| Skimmer / speed reader | 400+ WPM | 2.5 minutes or less |
So, most people take about 5 minutes to read 1000 words comfortably. But that’s not the whole story — context matters. Let’s go deeper.
2. What Is WPM and Why It Matters
WPM (Words Per Minute) measures how fast you can read or speak. A person’s WPM depends on:
- Text difficulty
- Familiarity with the topic
- Reading purpose (study, leisure, review)
- Language proficiency
The average adult reading speed is 200–250 WPM, but can range from 100 to 400+ WPM across individuals. At WordToTime.org, we use this variable to estimate reading, speaking, or listening durations with precision.
3. How Reading Speed Affects Reading Time
Below is a visual chart showing how long 1000 words take to read at different speeds:
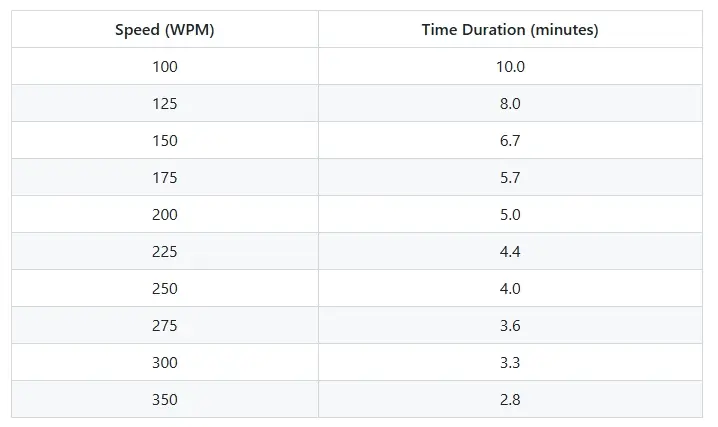
| Speed (WPM) | Time (minutes) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 10.0 |
| 125 | 8.0 |
| 150 | 6.7 |
| 175 | 5.7 |
| 200 | 5.0 |
| 225 | 4.4 |
| 250 | 4.0 |
| 275 | 3.6 |
| 300 | 3.3 |
| 350 | 2.8 |
💡 Pro Tip: Use this as a “time budget” when writing or preparing content. If your reader averages 200 WPM, every 200 words ≈ 1 minute of reading.
4. Reading Purpose Changes Everything
Different contexts require different reading speeds. Here’s how:
| Purpose | Typical WPM | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Careful study | 100–150 | Deep comprehension, annotation |
| Normal reading | 180–250 | Most nonfiction or web articles |
| Light reading | 250–300 | Casual fiction, news |
| Skimming | 350–450 | Looking for key ideas |
| Proofreading aloud | 120–160 | Slower due to articulation |
A 1000-word scientific article might take 8–10 minutes, while a light blog might only take 3–5 minutes.
5. Reading vs. Speaking Time
If you turn your text into spoken audio, the time increases. Speaking is slower — typically 125–160 WPM.
| Format | Average WPM | 1000 Words Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Silent reading | 200 WPM | 5 min |
| Reading aloud | 150 WPM | 6.7 min |
| Public speaking | 130 WPM | 7.7 min |
| Audiobook narration | 160 WPM | 6.2 min |
This is why WordToTime.org lets you choose between reading and speaking modes for accurate results.
6. Factors That Change Reading Time
Your actual time may vary due to:
- Language difficulty (academic vs everyday text)
- Font and formatting (dense text slows readers)
- Distractions and focus
- Reading on screen vs print
- Cognitive fatigue
Even mood affects reading speed — calm focus can boost WPM by 15–20%.
7. Visual Guide: Reading Speed Comparison
Below is an educational illustration comparing different readers and their times for 1000 words:
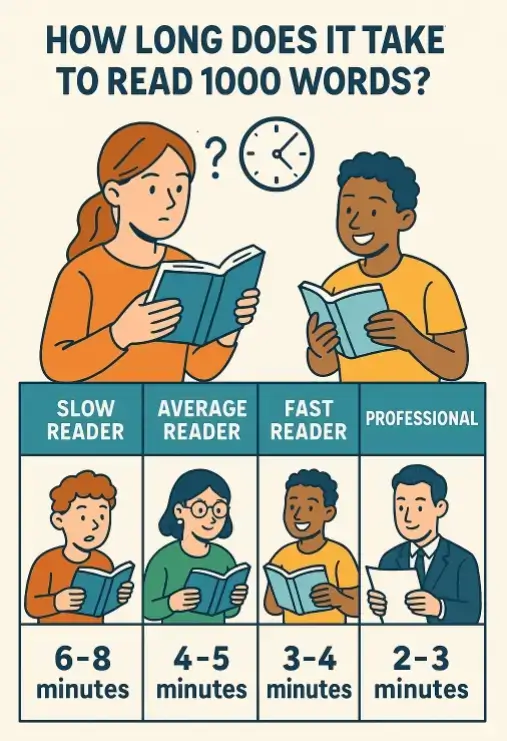

This visual shows:
- A slow reader taking 10 minutes, deeply focused on detail.
- A fast reader finishing in under 3 minutes, scanning key points.
- A comfortable average zone around 5 minutes — ideal for most web readers.
8. Formula: How to Calculate Reading Time
You can easily estimate reading duration with this simple formula:
Reading Time (minutes) = Word Count ÷ WPM
Example: If your WPM is 220, then 1000 ÷ 220 = 4.5 minutes.
To include a natural variation, add 10% for pauses or complexity:
Adjusted time = (Word Count ÷ WPM) × 1.1
So 1000 words ≈ 5 minutes — matching real-world results.
9. Using WordToTime.org for Accurate Estimation
Instead of calculating manually, visit 👉 WordToTime.org
You can:
- Paste any text
- Choose reading, speaking, or voice-over mode
- Adjust your average WPM
- Get instant time estimates with pause adjustment
Ideal for writers, teachers, narrators, and video creators.
10. Real Examples
| Content Type | Approx. Words | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1-page email | 300 | 1.5 min |
| Blog post | 1000 | 5 min |
| Whitepaper | 2500 | 12–14 min |
| Speech draft | 1200 | 8 min |
| Video script | 800 | 5 min |
This is why marketers and educators often design 5-minute reads — it fits most readers’ attention spans.
11. How to Improve Your Reading Speed
- ✅ Practice skimming for structure.
- ✅ Eliminate subvocalization (inner speech).
- ✅ Use a finger or pointer to guide eyes.
- ✅ Increase focus time (Pomodoro method).
- ✅ Take comprehension breaks every 10 minutes.
Many readers can improve by 25–50 WPM in just a few weeks.
12. FAQs About Reading Time
How long does it take to read 1000 words out loud?
About 6–8 minutes, depending on your speaking pace.
How long does it take to read 1000 words silently?
Roughly 4–6 minutes for most adults.
Does difficulty affect reading time?
Yes — complex texts can double your time.
How many pages is 1000 words?
~2 pages (double-spaced).
How can I calculate for any word count?
Use WordToTime.org — it handles both reading and speaking time.
13. Key Takeaways
- Average person: 5 min to read 1000 words
- Speaking is slower: 6–8 min for 1000 words
- Adjust for context, purpose, and reader focus
- Use WordToTime.org for fast, accurate results
14. Conclusion
Understanding reading time helps you write and plan better. Whether you’re optimizing a blog, designing training content, or preparing a speech, knowing how long it takes to read 1000 words keeps your audience engaged — without losing attention.
📘 Try it now on WordToTime.org — Paste your text, choose mode, and get precise results in seconds.