The Ultimate WPM Chart: Reading and Speaking Speeds Explained (with Visual Data)
Discover global reading and speaking speeds with our complete WPM chart. Learn how to calculate your Words Per Minute, compare across professions, and optimize your pace using WordToTime.org.
Have you ever wondered how fast people actually read or speak? You might read a blog in three minutes, while someone else takes seven — that difference comes down to WPM (Words Per Minute).
At WordToTime.org, we help you measure, understand, and apply your WPM rate to plan perfect scripts, speeches, or reading sessions.
This article gives you the most complete WPM chart, combining global averages, visual data, and real examples from professionals.
1. What Is WPM and Why It Matters
WPM stands for Words Per Minute — the number of words you can read, speak, or write in one minute.
It’s a universal benchmark that helps you:
- Estimate reading or speaking duration
- Measure comprehension vs speed
- Plan speeches and video scripts
- Optimize content for audience pacing
Example
If you read at 200 WPM, you can finish a 1000-word article in 5 minutes. If you speak at 130 WPM, the same text takes 7.7 minutes.
So WPM determines how long your content feels — and how well it fits time limits.
2. Average Global WPM: Reading vs Speaking
Here’s a visual overview of global average WPM ranges for both reading and speaking speeds:
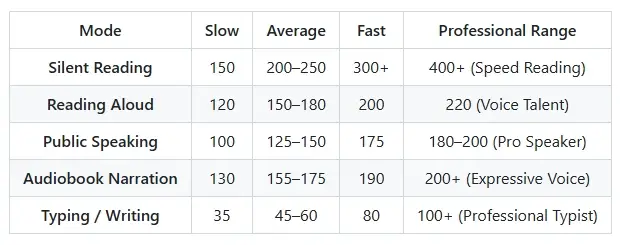
| Mode | Slow | Average | Fast | Professional Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silent Reading | 150 | 200–250 | 300+ | 400+ (Speed Reading) |
| Reading Aloud | 120 | 150–180 | 200 | 220 (Voice Talent) |
| Public Speaking | 100 | 125–150 | 175 | 180–200 (Pro Speaker) |
| Audiobook Narration | 130 | 155–175 | 190 | 200+ (Expressive Voice) |
| Typing / Writing | 35 | 45–60 | 80 | 100+ (Professional Typist) |
Key takeaway: Reading is naturally faster than speaking — about 30–40% quicker on average.
3. Understanding Reading Speed Variation
Your reading speed depends on what and how you read. Here are some common categories:
| Reading Type | Typical WPM | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Careful Study | 100–150 | Textbooks, Research Papers |
| Normal Reading | 180–250 | Blogs, Essays |
| Light Reading | 250–300 | News, Stories |
| Skimming | 350–450 | Scanning for info |
| Speed Reading | 500+ | Rapid visual reading |
💡 Fun fact: The world record for sustained reading speed exceeds 1000 WPM — but comprehension drops sharply above 400.
4. Speaking Speed: The Human Voice in Motion
Speaking involves breathing, rhythm, and audience connection. That’s why WPM tends to be lower.
| Speaking Context | Average WPM | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Conversation | 110–140 | Natural dialogue |
| Speech or Presentation | 120–150 | Balanced pacing |
| Radio Broadcast | 150–175 | Energetic, rhythmic |
| Podcast Hosting | 155–170 | Conversational yet clear |
| Voice-Over / Commercial | 160–180 | Concise, emotional |
| Audiobook | 155–175 | Expressive and consistent |
Good speakers adjust their pacing to audience attention, not just the clock.
5. Visual Data: WPM by Profession
Below is an educational-style visual chart comparing WPM across various professions:
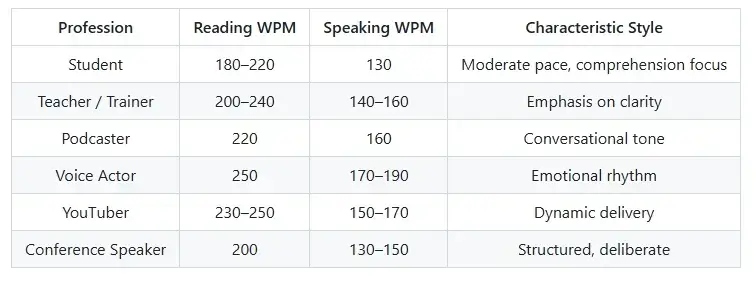
| Profession | Reading WPM | Speaking WPM | Characteristic Style |
|---|---|---|---|
| Student | 180–220 | 130 | Moderate pace, comprehension focus |
| Teacher / Trainer | 200–240 | 140–160 | Emphasis on clarity |
| Podcaster | 220 | 160 | Conversational tone |
| Voice Actor | 250 | 170–190 | Emotional rhythm |
| YouTuber | 230–250 | 150–170 | Dynamic delivery |
| Conference Speaker | 200 | 130–150 | Structured, deliberate |
This comparison shows how WPM varies across roles that rely heavily on verbal communication.
6. How to Calculate Your Own WPM
You can easily find your WPM with a simple test:
- Copy a 300–500-word passage.
- Read or speak it naturally.
- Time yourself with a stopwatch.
- Divide total words by minutes taken.
Formula: WPM = (Total Words ÷ Time in Minutes)
Example: If you read 450 words in 2 minutes → 225 WPM.
✅ Try this instantly using the WordToTime.org Speed Test Tool — it auto-detects your reading and speaking rates.
7. WPM and Duration Relationship
The relationship between word count and time is direct:
Time (minutes) = Word Count ÷ WPM
Here’s a mini reference table for quick estimation:
| Words | 100 WPM | 150 WPM | 200 WPM | 250 WPM | 300 WPM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 5.0 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 1.7 |
| 1000 | 10.0 | 6.7 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 3.3 |
| 1500 | 15.0 | 10.0 | 7.5 | 6.0 | 5.0 |
| 2000 | 20.0 | 13.3 | 10.0 | 8.0 | 6.7 |
That’s why WordToTime.org is built around this formula — it simplifies time estimation for any script.
8. Using WordToTime.org to Measure WPM
You can:
- Paste your text
- Adjust WPM or use the built-in test
- Instantly see your estimated time
The tool dynamically calculates reading and speaking durations with pause factors for natural realism.
9. Tips to Improve Your WPM
- ✅ Eliminate subvocalization (silent inner voice).
- ✅ Expand vocabulary to process words faster.
- ✅ Read in blocks (not word-by-word).
- ✅ Maintain good eye movement rhythm.
- ✅ Practice with varied material — fiction, news, technical docs.
Advanced readers can increase their speed by 20–50 WPM while maintaining comprehension.
10. Why WPM Is Crucial for Creators
For content creators, educators, and voice artists, knowing WPM helps:
- Plan duration before recording
- Maintain consistent pacing
- Synchronize voice to visuals
- Meet time-based project goals
It’s not just a metric — it’s a creative timing tool.
11. FAQs About WPM
What’s a good WPM for reading?
200–250 WPM is typical for adults; 300+ is above average.
What’s a professional WPM for speakers?
Most speakers range between 125–160 WPM.
Do languages change WPM?
Yes. For example, English averages 200 WPM, while Mandarin averages closer to 160.
Does comprehension drop with speed?
Above 400 WPM, understanding tends to decline.
How do I measure my WPM accurately?
Use WordToTime.org for a real-time test.
12. Conclusion
Understanding your Words Per Minute is key to mastering communication — whether you’re writing, reading, or speaking.
With the Ultimate WPM Chart, you now know how to:
- Compare reading vs speaking speeds
- Estimate durations precisely
- Adjust your pacing for your audience
⏱️ Try the WPM Test Tool today at WordToTime.org and discover your personal reading and speaking rhythm.